SPSS OMS Tutorial – Creating Data from Output
SPSS OMS (short for Output Management System) can convert your output to SPSS datasets. As we'll demonstrate in a minute, this can save you huge amounts of time, effort and frustration.
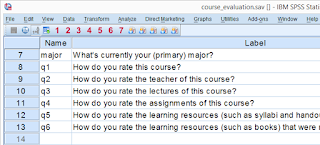
We recommend you follow along by downloading and opening course_evaluation.sav, part of which is shown below.
Today’s Challenge
Some client wants to see charts holding correlations of q2 through q6 with q1 for each study major (psychology, anthropology) separately as shown here. This request -not unusual in market research- typically makes novice SPSS users
panic,
run the correlations in SPSS,
copy/paste everything into Excel sheets and
generate the charts one by one.
Unknown to many SPSS users, there's a much -much- faster way for getting this job done. It's called OMS.
Step 1: Split File
We'd normally always start with a routine data inspection but that's been done for you in this case. Now, a fast way for just running the desired correlations is by using SPLIT FILE. The syntax below shows how to do so.
Step 2: OMS Control Panel
Right, we created our correlations but they're in our Output Viewer window. We can't create charts from tables in our output window so we need this correlation table in data view instead.
We'll do just that by navigating to Utilities SPSS Menu Arrow OMS Control Panel which is shown below.
We'll follow the steps in the screenshot: we select our correlation table in the left half of the dialog.
It's a best practice to always specify an ID here. In this case, “corid” is short for “correlation id”
We then select New Dataset in the right half of the dialog. “cords” is short for “correlation dataset”.
Clicking Paste triggers a popup dialog confirming our OMS request. Just ignore it.
Clicking Ok then generates the first block of the syntax below. We then (manually) added two lines to it.
SPSS OMS Syntax Example
SPSS OMS Syntax - How Does It Work?
The next figure explains how our syntax basically works. In a nutshell,
the OMS command has SPSS monitor selected output following it so
our correlation table is captured by the OMS.
OMSEND then stops SPSS from monitoring output and create our desired correlations dataset.
SPSS OMS - OMS Syntax Explained
Result
SPSS OMS -
We now have our correlation matrix in an SPSS dataset, which allows us to run charts on it. We'll prepare these data a tiny bit before doing so with the syntax below.
*1. Activate newly created correlations dataset.
dataset activate cords.
*2. Delete all rows that don't hold correlations.
select if char.index(var3,'Pearson') > 0.
execute.
*3. Split file by var1
smile emoticon
study major).
sort cases by var1 howdoyouratethiscourse.
split file by var1.
Step 3: Creating Our Charts
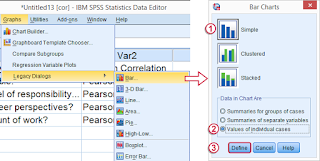
We'll now create our desired charts by following the figure below. Since we're using SPLIT FILE, we need only one single command for creating all charts at once.
SPSS OMS -
In the second dialog (below), choose a nice main title for your charts. We decided upon “Correlations with Course Rating”.
SPSS OMS -
Following these steps results in the syntax below. Running it generates all desired charts.
SPSS Bar Chart Syntax Example
*Create actual charts.
GRAPH /BAR(SIMPLE)=VALUE(Howdoyouratethiscourse) BY Var2/title 'Correlations with Course Rating'.
Step 4: Prettifying our Charts
We now have the charts we wanted. A nice trick to make them look great with little effort is creating a chart template for them.
We double click just one of our charts and transpose it as shown below.
SPSS OMS -
Next, we change the colors, fonts, layout, everything in our first chart until it looks nice. Then navigate to File SPSS Menu Arrow Save Chart Template as explained in SPSS chart templates.
SPSS - Creating Pretty Charts
Finally, we activate the chart template we just created (step 3 below, first set path to .sgt file correctly). We then rerun the GRAPH command we pasted and ran previously and - there you go - five pretty charts in a split second.
If you ever get a similar request for different data, you can now rerun your syntax on it and you'll be done in seconds. As a bonus, you can probably (edit and) reuse your chart template other bar charts too.
Final Syntax Using Chart Template
*1. Apply variable label (shows up in chart subtitle).
variable labels var1 "Study Major".
*2. Suppress excessive decimal places.
formats howdoyouratethiscourse (f1).
*3. Activate newly created chart template (set path appropriately).
set ctemplate 'my-project-folder\my-template.sgt'.
*4. Rerun all graphs at once with chart template.
GRAPH /BAR(SIMPLE)=VALUE(Howdoyouratethiscourse) BY Var2/title 'Correlations with Course Rating'.
*5. Switch off chart template for any future graphs.
set ctemplate none.
Final Result
SPSS OMS -
Final Notes
SPSS OMS can be a tremendous time saver. Today's tutorial redirected a single correlation table to an SPSS dataset but you can very easily create a single dataset holding output from 1,000 or more output tables. In fact, we did just that in the simulation studies we presented when explaining the basic idea behind ANOVA, regression and the chi-square test. In these studies we basically
used one OMS command for capturing all ANOVA tables,
ran ANOVA on 1,000 random samples from a population data file,
ran OMSEND for creating a dataset with 1,000 F-values and
created a histogram for visualizing our sampling distribution.
As we see, SPSS OMS opens up a lot of possibilities. We hope it'll help you save time and effort as well!